AD = C + I + G + (X – M)
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 05 julho 2024

So by the expenditure model our National Income is equal to our collective spending (Aggregate Demand). Let’s see what influences each element of this important equation.
Aggregate Demand Definition, Importance, Components, Curve
1649484380_8179052.png

Tax causes decrease in aggregate demand

Solved 12) Based on textbook Question 14.6. The aggregate

SOLVED: HOMEWORK Consider the following macroeconomic system where C, I, G, X, M represent respectively, consumption expenditures, investment expenditures, government expenditures, exports, and imports. Yd and Y denote the disposable income and
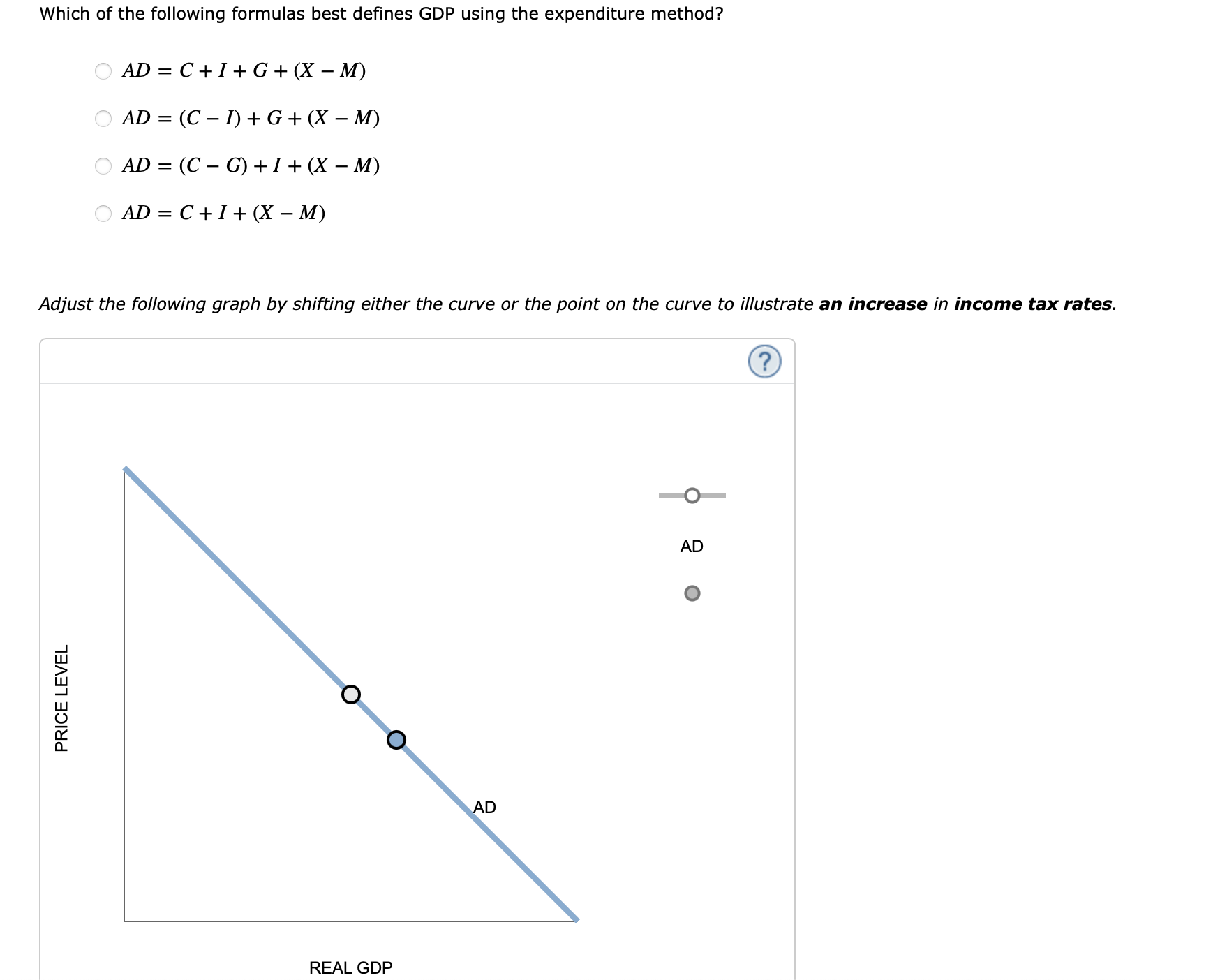
AD = C + I + G + X - M - Economics Help

Aggregate Demand – ECONFIX

3.2 (Macro) Determinants of Aggregate Demand (AD): Consumption, Investment, Government, Net Exports

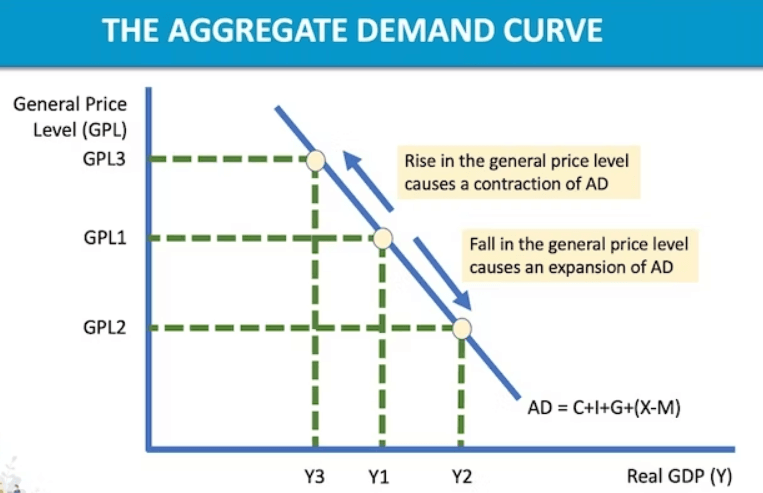
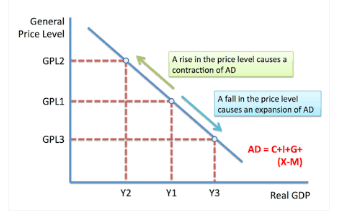
3.3: Macroeconomic Models. Aggregate Demand Components AD=C+I+G+X-M AD=C+I+G +X-M How does the AD curve (and diagram labels) differ from a simple demand. - ppt download
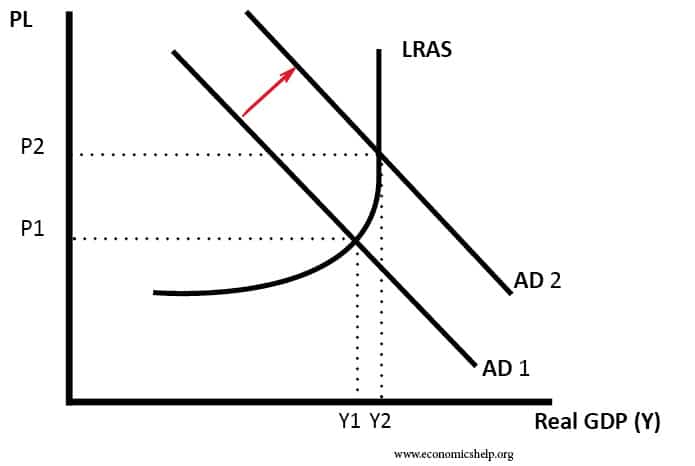
AD = C + I + G + X - M - Economics Help
Solved] Which components of GDP (C,I,G,X,M) would be affected by the
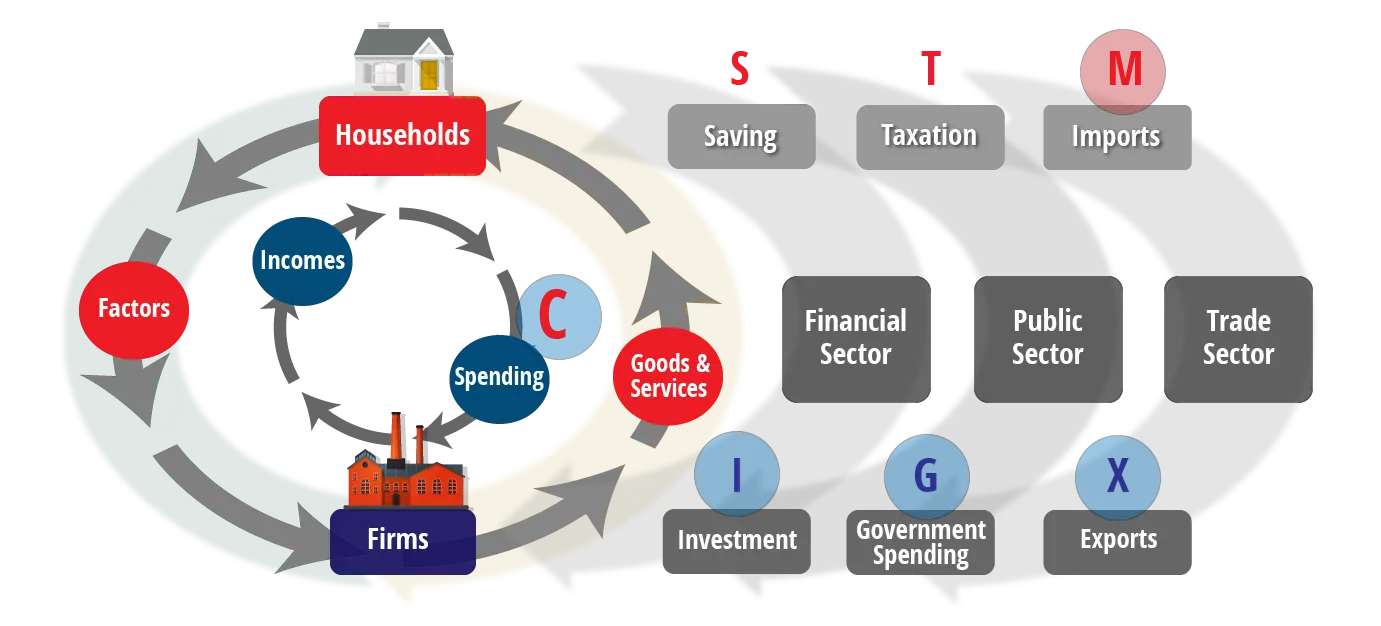
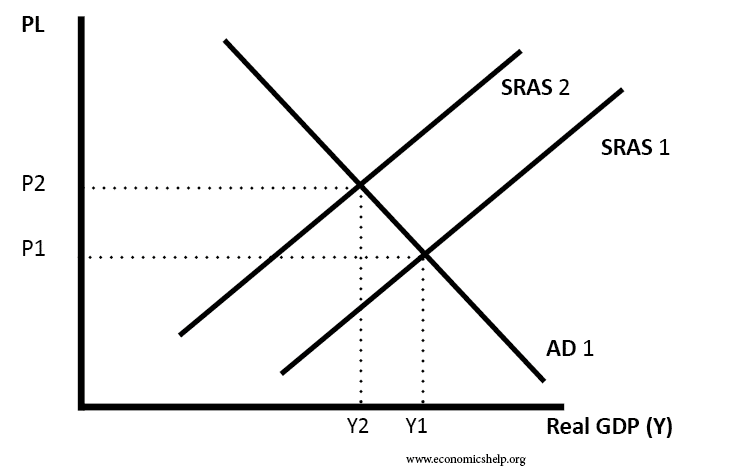
The AD-AS model
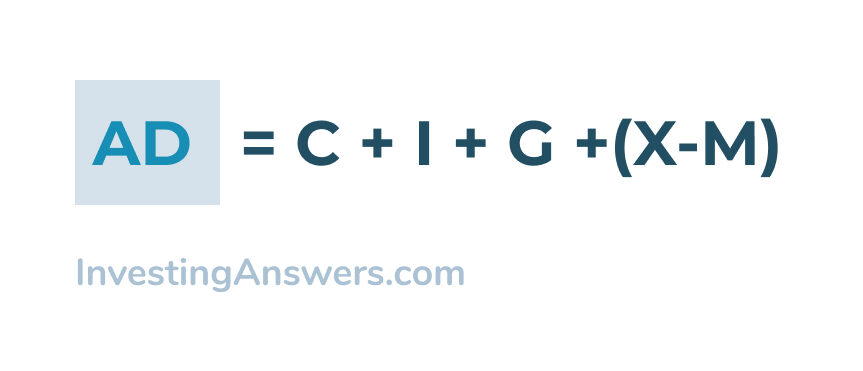
Aggregate Demand Definition and Examples

Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply and Curves
Recomendado para você
-
 gross domestic product or GDP formula are consumption, business investment, government spending, and net exports 29565485 Vector Art at Vecteezy05 julho 2024
gross domestic product or GDP formula are consumption, business investment, government spending, and net exports 29565485 Vector Art at Vecteezy05 julho 2024 -
 INTENSITY FORMULAE FOR THE ZEEMAN EFFECT (CHAPTER XV) - The New Quantum Mechanics05 julho 2024
INTENSITY FORMULAE FOR THE ZEEMAN EFFECT (CHAPTER XV) - The New Quantum Mechanics05 julho 2024 -
![National Savings: Formula, Its Importance, How To Calculate It - Penpoin. [2023]](https://i0.wp.com/penpoin.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/National-Savings-Formula-Its-Importance-How-To-Calculate-It.jpg?fit=1632%2C960&ssl=1) National Savings: Formula, Its Importance, How To Calculate It - Penpoin. [2023]05 julho 2024
National Savings: Formula, Its Importance, How To Calculate It - Penpoin. [2023]05 julho 2024 -
 The Balance of Payments and Capital Flows05 julho 2024
The Balance of Payments and Capital Flows05 julho 2024 -
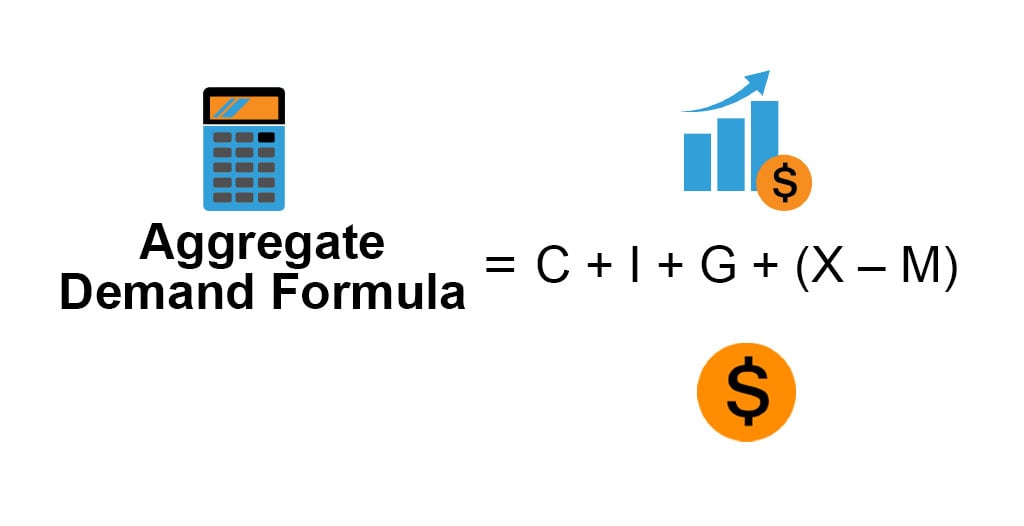 Aggregate Demand Formula Calculator (Examples with Excel Template)05 julho 2024
Aggregate Demand Formula Calculator (Examples with Excel Template)05 julho 2024 -
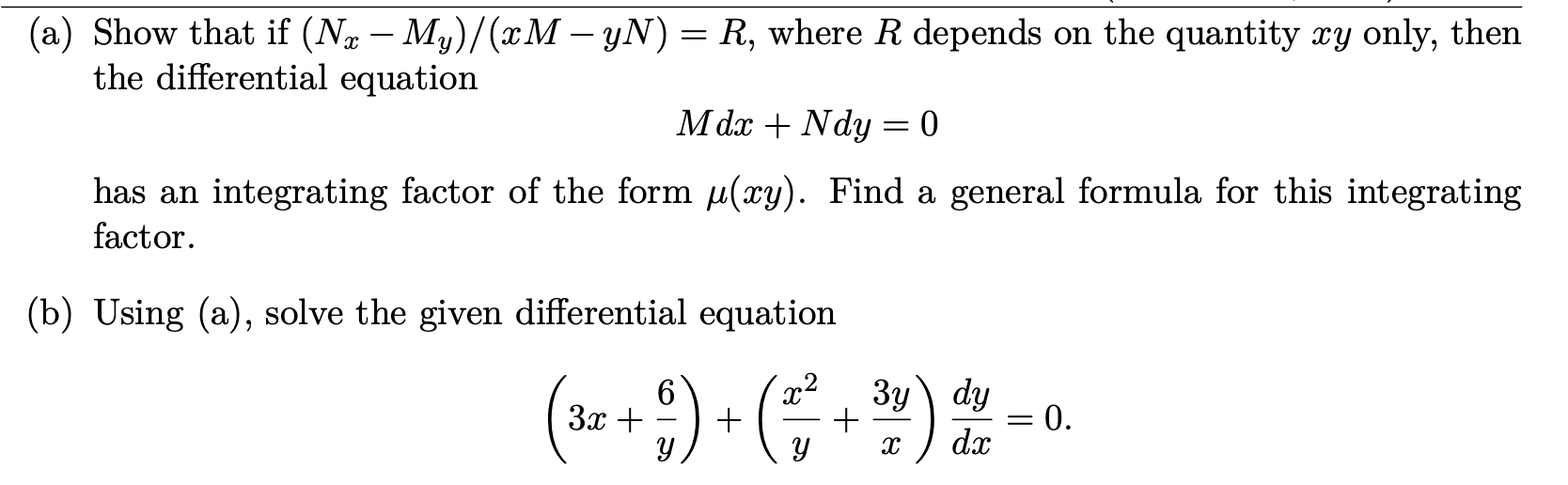 Solved (a) Show that if (N. – My)/(xM – YN) = R, where R05 julho 2024
Solved (a) Show that if (N. – My)/(xM – YN) = R, where R05 julho 2024 -
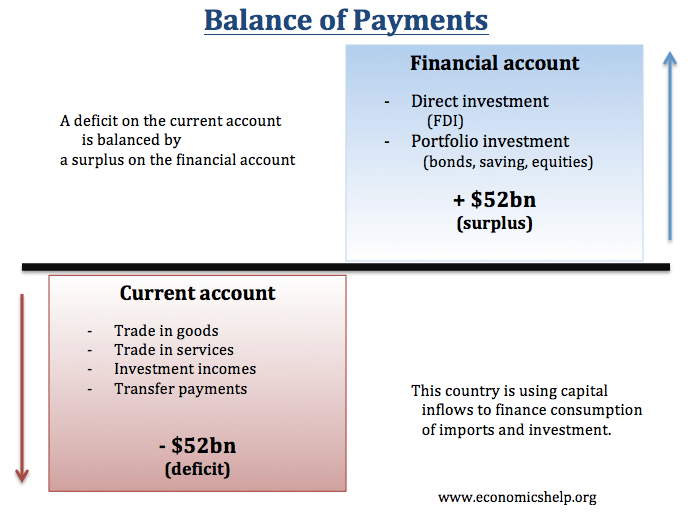 Current Account = Savings - Investment - Economics Help05 julho 2024
Current Account = Savings - Investment - Economics Help05 julho 2024 -
 Characterization and Quantification of Oligosaccharides in Human Milk and Infant Formula05 julho 2024
Characterization and Quantification of Oligosaccharides in Human Milk and Infant Formula05 julho 2024 -
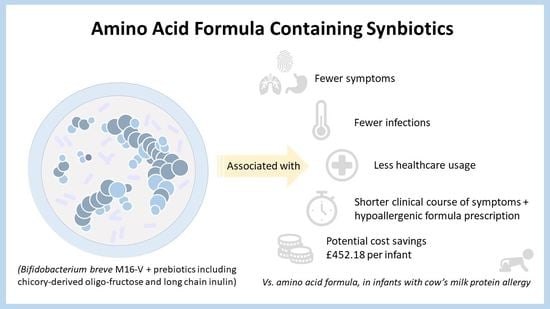 Nutrients, Free Full-Text05 julho 2024
Nutrients, Free Full-Text05 julho 2024 -
 GCSE Maths - What on Earth is y = mx + c #6705 julho 2024
GCSE Maths - What on Earth is y = mx + c #6705 julho 2024
você pode gostar
-
Need help, colors glitching - Help - Aseprite Community05 julho 2024
-
 Skull & Bones - Rotten Tomatoes05 julho 2024
Skull & Bones - Rotten Tomatoes05 julho 2024 -
 When does your Chess Rating Starts ? – Legend Chess Academy05 julho 2024
When does your Chess Rating Starts ? – Legend Chess Academy05 julho 2024 -
![GTA : Vice City - platinum [Playstation 2]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/W/MEDIAX_792452-T2/images/I/61e6sU9SIzL._AC_UF1000,1000_QL80_.jpg) GTA : Vice City - platinum [Playstation 2]05 julho 2024
GTA : Vice City - platinum [Playstation 2]05 julho 2024 -
 Yes, Precure 5 Gogo /Smile Precure /Kirakira Precure a la mode collab edit . : r/precure05 julho 2024
Yes, Precure 5 Gogo /Smile Precure /Kirakira Precure a la mode collab edit . : r/precure05 julho 2024 -
 mogulcloudgamefreegemshackhowtogetfreegemsinmogulcloudgame's NFT Collection05 julho 2024
mogulcloudgamefreegemshackhowtogetfreegemsinmogulcloudgame's NFT Collection05 julho 2024 -
 Buy Cardcaptor Sakura Manga online05 julho 2024
Buy Cardcaptor Sakura Manga online05 julho 2024 -
 Ilha do Terror” é atração no Shopping Cidade Sorocaba - Jornal Z Norte05 julho 2024
Ilha do Terror” é atração no Shopping Cidade Sorocaba - Jornal Z Norte05 julho 2024 -
 Square Off Swap Smart Automated Chess Board Game05 julho 2024
Square Off Swap Smart Automated Chess Board Game05 julho 2024 -
 Boneco Pokémon Torchic + PokéBola SUNNY 2606 - Sunny - Brinquedos e Games FL Shop05 julho 2024
Boneco Pokémon Torchic + PokéBola SUNNY 2606 - Sunny - Brinquedos e Games FL Shop05 julho 2024